Server virtualization is the cornerstone of the datacenter because with server virtualization, it is possible to use management and control facilities and tools, and it is practically impossible to provide administrative services. In server virtualization, various goals are pursued; one of them is managing and dividing the hardware resources of a physical server (Host) between several virtual servers. But the primary purpose of server virtualization is High Availability (HA); the purpose of high availability is 24/7 service. To reach this, virtual machines are distributed among several physical servers (Host) so that in case of failure of one of the hosts, other hosts can still respond to the hardware requirements of the machines. In the discussion of virtualization, the monitoring, management, and control of hardware resources are provided to the Hypervisor, and it is the Hypervisor that provides the resources to the virtual machines according to the applied policies.

Importance of virtualization
Server virtualization can benefit organizations, provided that defined standards implement it. Server virtualization and primary and vital benefits can reduce datacenter maintenance costs, including electricity consumption, cooling system costs, and physical and management integration. But the main advantages of server virtualization are High Availability, Fault Tolerance, Distributed Resource Scheduler, and Distributed Power Management because most services and organizational applications are interdependent. If one or more benefits were lost, it would affect the entire organizational structure, and users couldn’t do their administrative activities. The best solution for datacenter integration and management is to use server virtualization and its HA, FT, DRS, and DPM capabilities.
High Availability
One of the significant concerns in datacenter discussions is that if several virtual machines run on a physical server, all virtual servers will fail if the physical server fails. What is the solution?
HA service is the answer to this problem. The function of this technology is that two or more physical servers are first placed in a cluster. Virtual machines are distributed on the physical servers of the cluster. If one of these servers fails, the virtual machines on the server are moved to other servers in the cluster. In this way, virtual machines can serve 24/7.
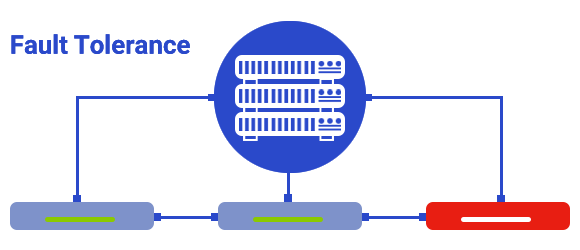
Fault Tolerance
Suppose one of the physical servers fails in a cluster where HA is enabled. In that case, its virtual machines will be reset before being transferred to the second physical server and will be out of service for a short time which may last up to 3 minutes and causes all the unsaved data in the RAM will be lost.
FT technology has solved this problem. The function of this technology is that in the clusters where FT is active, a copy of the running virtual machines is also running on a second server. When a physical server shuts down, the virtual machine mirrored on the second server is immediately replaced without the slightest interruption, and the end user will not notice this.
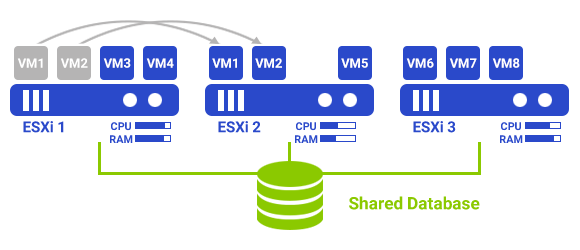
DRS (Distributed Resource Scheduler)
The ability to move virtual machines to create suitable conditions is called DRS. The work basis of DRS is that if several virtual machines are in one of the physical servers, server resources such as CPU and RAM are specified in a specific ratio for them. Suppose one of the virtual machines faces a lack of resources while other virtual machines have yet to use their resources, in this situation, using DRS. These resources are assigned to the virtual machine with fewer resources. In fact, by using DRS, the available resources for the cluster are controlled, and it automatically makes the necessary changes to achieve optimal conditions between all virtual machines.
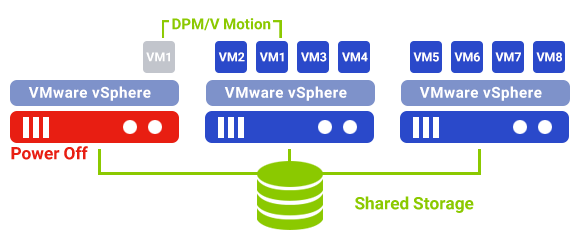
DPM (Distributed Power Management)
Combining physical servers with virtual machines that share physical host resources can reduce hardware maintenance costs and power consumption. DPM provides additional energy savings by consolidating workloads even during periods of low resource usage. Virtual machines are moved to lower expenses, and unnecessary ESXi hosts are shut down.
DPM saves energy by using cluster capacity with an appropriate size according to the business requirements. When CPU and memory resources are used, DPM recommends that ESXI hosts be unloaded and shut down. When CPU or memory resource usage increases or additional host resources are required, DPM recommends restarting ESXi hosts.
DPM does not shut down hosts with FT-capable VMs until they are manually migrated using vMotion because DRS does not automatically migrate FT-capable VMs.

